An IPTV encoder takes the content from the video source, whether it’s a live recording from a camera or an uncompressed video file from a digital storage device, and encodes it for distribution over the Internet.
Day by day, new encoders are coming to the market with new technologies and features. The newest encoders are utilizing the latest high-quality, low-bitrate H.265 High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) technologies. Also, it allows content creators to encode HD content while maintaining the current data bandwidth and storage requirements they’ve enjoyed with previous generation H.264 encoders. This allows operators to improve video quality without having to massively upgrade their entire network bandwidth and storage.
Standard TS/IP output ensures that the encoder’s output can be fed into the existing broadcast infrastructure. To be used as input to modulators, multiplexers, IRDs, and storage servers.
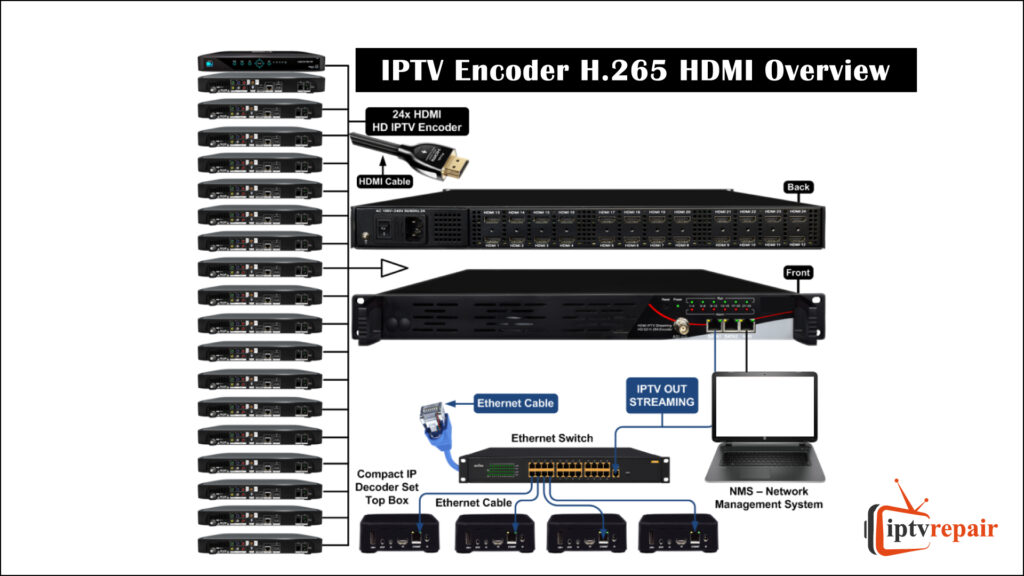
What is IPTV Encoder?
H.265 HDMI is basically called Video Encoder/IPTV Encoder/RTMP Live Encoder and is likely a professional HD Audio and video encoding device that contains powerful functionality. It supports both H.264/H.265 encoding, and 4 streams of data, and is equipped with 1 HDMI channel input support to H.265/H.264 main profiles video code format and MP3/AAC audio code format respectively.
From any HDMI input source, it can generate H.264/H.265 encoding streams compliant with HTTP/RTMP/RTSP/TS/UDP/HLS/FLV protocols as well. Its high integration and cost-effective designs make this device widely applied in Video Streaming Encoder, IPTV, Broadcast, Live streaming, Video conferences, Network Video recording, Remote Education, etc.
What are the Features of IPTV Encoder?
- Supports 1x channel 4K or 4x channels HD encoding
- Ultra-low latency of up to 10ms
- Multiple video resolutions including 2160p, 2160i, 1080p, 1080i, 720p, 720i, 480p, 480i
- Supported inputs: 3G/HD/SD-SDI
- Internal Time Base Correction (TBC)
- MPEG-1 Layer II & AAC LC audio encoding, AC3 pass-through
- Up to 4x stereo audio encoding
- 10/1000M TS/IP SPTS and MPTS
- UDP, RTP/UDP, Multicast/Unicast, HLS, RTMP, SRT streaming, IGMPv2,
- Built-in re-multiplexer
- Supports VBR and CBR encoding modes
- Remote Control and Supervision with SNMP, HTTP WEB
- HDMI video up max to 1080P 60fps
- H.264/H.265 main profile video code
- MP3/AAC Audio Compression
- 4 streams can transmit with different protocols
- Adjustable Bit Rate 0.16~32 Mbps
- Low power consumption (less than 5W)
- Low network delay (less than 200ms)
Key Features of Encoder in Brief:
- Distribute any HDMI Full HD Video DIRECTLY to unlimited Smart TVs, Mobile Phones, Tablets, PCs, IP Box
- IPTV Over Lan – WiFi – Internet
- Streams Directly on Any Smart TV – Add More VeCASTER units for More Channels
- Change the Channel on the TV through the TV Remote Control
- Tuners selection: DVB-S/S2, DVB-T, DVB-C, ISDB-T, ATSC
- 1 Channel 4K or 4 channels HD encoding
- Inputs: four 3G-SDI, 4/8/12 HD-SDI, 4/8/12 HDMI, supporting HDCP
- HD/SD-SDI, HDMI, Composite, ASI and IP Outputs
- SD: PAL/NTSC, HD: 720p, 1080i, 1080p.
- Encoding of up to 2160p
- Built-in “Gigabit Server” for streaming directly to 100 simultaneous player
- Can also stream on Youtube, Akamai, Wowza, and others
- It has “Dual Simultaneous Encoders and Scalers” to create 2 versions of the same channel
- Optimize for TV play and mobile Play simultaneously
- UDP, RTP/UDP, Multicast, Unicast, IGMPv2, ARP, SRT streaming
- Simultaneous Live Out in M3U/HTTP/RTMP/RTSP/TS/UDP/HLS/FLV protocols, H264, Mpeg1L2/AC3/AAC Audio Encoding
- Simultaneously works Anywhere
How does the IPTV Encoder work?
IPTV encoders play an essential role in turning television content over IP networks. Here’s a simplified evaluation of the way an IPTV encoder works:
1. Source Input: The encoder takes in audio and video signals from diverse sources, including satellite TV for PC receivers, cameras, or cable packing containers. These assets offer the uncooked content that is to be distributed over the IPTV community.
2. Compression: One of the primary capabilities of the encoder is to compress the audio and video content. Compression reduces the scale of the statistics even as retaining is satisfactory. Popular video compression requirements used encompass H.264 and H.265 (MPEG-4 and HEVC, respectively).
3. Packetization: After compression, the encoder breaks down the audio and video streams into smaller information packets. These packets are formatted in keeping with unique streaming protocols, including RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) or MPEG-TS (MPEG Transport Stream).
4. Metadata and Synchronization: Metadata, which includes records approximately the content, timestamps, and other information, is brought to the information packets. This metadata helps receivers nicely decode and display the content material. Synchronization ensures that audio and video live in sync for the duration of playback.
5. Encoding Settings: The encoder permits directors to configure diverse settings, which include video resolution, bitrates, and encoding profiles. These settings can be adjusted to optimize the streaming experience primarily based on community bandwidth and viewer alternatives.
6. Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (Optional): Many encoders support adaptive bitrate streaming. This means that multiple versions of the same information can be produced in different attributes. Viewers’ devices can dynamically switch between these versions based on their internet connection speed, to ensure smooth playback.
7. Streaming Protocol: The encoder uses streaming protocols such as RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol), HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), or MPEG-DASH to transfer the encoded content over an IP network
8. Network Delivery: The encoded and packetized content is then transmitted over the IPTV network. This can be multicast or singlecast depending on the configuration of the network and the number of viewers.
9. Customer Devices: IPTV set-top boxes, smart TVs, computers, or mobile devices that receive uploaded content. These devices use IPTV client software to decode packets, reconstruct audio and video, and display them on the viewer’s screen.
10. Content Protection: Some encoders include encryption and digital rights management (DRM) to protect information from unauthorized access and piracy.
In summary, IPTV encoders take raw audio and video input, compress it, format it for transmission, add the necessary metadata, and send it to viewers’ devices via IP networks This process enables television distribution content well over the Internet or dedicated IP networks.
Market Coverage of Encoders
- IPTV
- Video Conference
- Digital Signage
- Live Broadcast
- Recording System
- Replace HD Video Capture Card
- Hotel TV system
- Teaching/Campus Broadcast
- NVR(Net Video Recorder)
Hope this information will help you to gain knowledge about Encoders or IPTV Encoders. For more articles like this, follow IPTVJournal.
Conclusion
IPTV encoders are essential components of the IPTV ecosystem, serving to compress, encapsulate, and transmit audio and video content over IP networks. They play a key role in providing high-quality television content to viewers, in supporting features such as adaptive streaming and content protection, and ultimately in today’s IPTV experience.
